The differences between HDD and SSD hard drives – Hard drive is a key component of laptops and desktops. Behind its very technical aspect, choosing a hard drive is relatively simple. There is little room for error and you shouldn’t worry about buying the “wrong” hard drive. Let’s see in more detail the aspects to consider when choosing your hard disk and SSD.
External hard drives HDD and SSD
An external hard drive (or DDE) is a portable storage device typically connected to a computer via USB, FireWire eSATA, or wireless connection. External hard drives generally have a high storage capacity and are commonly used to store data and perform backups.
Using an external hard drive simply requires connecting the drive cable to your computer, although in some cases there may be compatibility issues with the operating system.
These types of hard drives can store a large number of files, music, videos or pictures due to their high storage capacity.
HDD (hard disk)
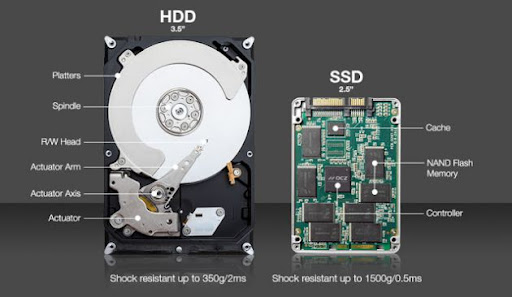
The hard drive of a computer plays the essential role of storing and retrieving information. HDD hard drives (for Hard disk in English) are the most used, especially for desktop computers. These disks, internal or external to the computer, consist of one or more mechanical disks that read and write information on the disk.
Solid State Drive (SSD)
SSD hard drives use flash memory (not mechanical like HDDs) to store information. They offer longer life and superior performance to HDD hard drives. However, the latter have generally higher storage capacity at a lower cost.
Differences between HDD and SSD hard drive
SSDs and hard drives do essentially the same job: they boot the operating system, store applications and personal files. But each has its specificities (storage capacity, price, speed, etc.).
The price of SSD and HDD
SSDs are more expensive than HDDs in terms of euros per gigabyte. A 1TB 2.5 ″ internal hard drive costs on average between 50 and 70 euros. It will take around 300 euros for an SSD of the same capacity.
Storage capacity: SSD vs HDD
Although there are SSDs of several TB (up to 16 TB), these are rare and expensive. HDDs from 500GB to 1TB are the order of the day and are considered basic capacities. As for SSDs, the early prices offer a storage capacity of around 128GB.
Speed of execution
Speed of execution is the strong point of SSDs. A computer with SSD will boot up in under a minute (seconds for most) and be faster for starting and running applications, as well as for transferring files. Whether you use your computer for leisure, school or work, speed is a primary factor in a computer.
Read Also : 5 Solutions How To Increase PC Performance
Durability and resistance
An SSD has no moving parts, so it is more shock resistant than an HDD hard drive. Some hard drives external still have protection to deal with this problem (such as Sturdy, resistant to water, dust, shocks and falls).
Market availability
HDDs are the most common and most accessible although SSDs are starting to be more and more present especially in small portable netbooks and ultrabooks with storage capacities ranging from 256 to 516 GB for the most part.
Sizes and shapes of a hard drive
SSDs are renowned for their performance. If you decide to opt for an SSD in favor of a hard drive, be aware that there are two common sizes of SSD. The 3.5 “is suitable for desktop use while the 2.5” is designed for laptop use (with more limited space).
Note that it is possible to connect a 2.5 “SSD to a 3.5” bay using an adapter, but the reverse is not possible. If you buy a laptop, the default size of this SSD will therefore be 2.5 ”. In this case it is recommended to look at the other SSD technical specifications.
First let’s think about the noise: internal or external HDD hard drives are relatively noisy. Even the quietest HDD will make a slight noise due to the arm and disc rotation. Thanks to their flash memory, SSDs produce practically no noise.
Then comes the power consumption: an SSD shouldn’t consume electricity to spin a platter. It is therefore less energy-intensive than its colleague. This lower power consumption translates into several minutes / hours of extra battery life.
SRT hard drives SSD / HDD
Some manufacturers have implemented a solution to couple a flash memory to a mechanical HDD. These “hybrid” models combine the storage capacity of an HDD and the performance of an SSD for a slightly higher price than a conventional hard drive. Flash memory serves as a buffer for frequently used files to speed up the launch of important applications.
There are also other technologies for combining an HDD and SSD on the same computer, such as SRT technology (Intelligent Response Technology) from Intel. The SRT uses the SSD as a cache to boot the system or start programs faster.
Although SSDs are increasingly democratized, they remain expensive but efficient alternatives to HDDs.
HDD hard drives prevail over the issue of price, storage capacity and availability in the market.
As for SSDs, they are definitely faster, more robust, more compact and less noisy. SSD hard drives are therefore an option of choice for laptops.