What is Natural Gas

Natural gas (also known as fossil gas; sometimes just gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of hydrocarbon gas consisting primarily of methane, but commonly includes varying amounts of other higher alkanes, and sometimes a small percentage of carbon dioxide, nitrogen, hydrogen sulfide, or helium.
It is formed when layers of decomposing plant and animal matter under the surface of the Earth are exposed to intense heat and pressure over millions of years. The energy that the plants were originally derived from the sun is stored in the gas in the form of chemical bonds.
Shale Gas
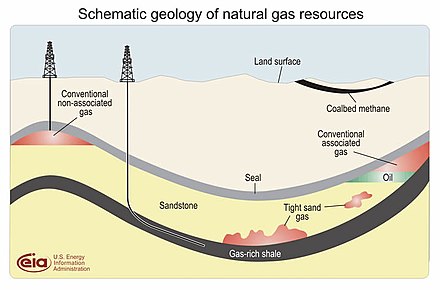
Shale gas is a natural gas contained in shale deposits to be trapped. Shale gas has since the beginning of this century become an increasingly significant natural gas source in the United States, with interest spread to future gas shales worldwide. Shale gas supplied just 1% of U.S. gas output in 2000. It was more than 20% by 2010, and the U.S. Energy Information Administration forecasts that 46% of the US natural gas supply would come from shale gas by 2035.
Some analysts expect shale gas to rise dramatically worldwide. China has the largest shale gas supply estimated in the world.
Application of natural gas
- Industrial heating and desiccation fuel
- Fuel for the operation of power stations for public and industrial use
- Household fuel for cooking, heating, and hot water supplies
- Fuel for environmentally friendly vehicles with compressed or liquid natural gas
- Raw material for synthesizing chemicals
- Raw material for large-scale production of gas-to-liquid (GTL) fuel
Where are we going to find it?
Technological advances, an accessible and abundant domestic resource, and the world’s largest and most reliable supply infrastructure have created a fundamental shift in the natural gas market, providing an opportunity to meet significant new demand at affordable prices well into the future.
In 2017, the potential gas committee (Colorado School of Mines) in coordination with the American Gas Association (AGA) released a biennial report at the end of 2016: potential natural gas supply in the United States, which found that the United States still has a technically recoverable natural gas resource base of 2,817 trillion cubic feet (Tcf).
Delivery and storage of natural gas
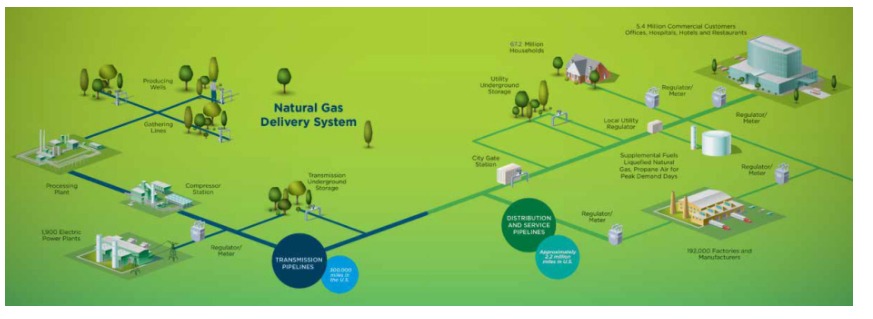
Delivery of natural gas from natural gas and oil wells to consumers requires a number of infrastructure assets and processing steps, including several physical transfers of custody. The supply infrastructure for natural gas can be grouped into three categories:
- Processing process
- Transportation of goods
- Storage of goods
There are three segments of the natural gas industry are involved in delivering natural gas to the consumer from the point of production.
- Production companies are exploring, drilling and extracting natural gas from the ground.
- Transmission companies operate pipelines linking gas fields to major consuming areas.
- Distribution companies are local utilities that supply natural gas to the customer.
Natural Gas Pipeline Systems
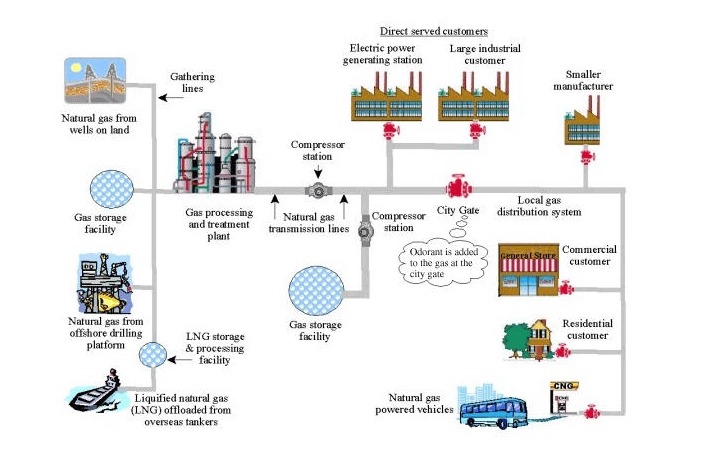
Natural gas pipeline systems provide a clean and efficient energy source, from the well to the consumer. There are essentially three main types of pipelines along the transport route: collection systems, transmission systems and distribution systems.
Collecting pipeline systems collect raw natural gas from wells of production. Transmission pipeline systems transport thousands of miles of natural gas across many parts of the United States of America.
Natural gas pipeline systems can be found in thousands of communities from coast to coast, distributing natural gas to our homes and businesses through mainland and service lines.
The gas service tube used in the pipeline systems can vary from 2 to 42 centimeters in diameter, with the exception of gas service lines and the gas service lines are normally 1⁄2 cm to 2 cm in diameter.
The pipeline systems for the collection and transmission of natural gas are made from steel pipes. However, the distribution systems of natural gas were made of various materials including cast iron, steel, copper and plastic tubing. For gas delivery systems, the plastic tube is currently most widely mounted.
Many different corporations own and run natural gas pipeline systems. In principle, federal and state regulations control the location, building and operation of those Systems.
Natural Gas In Your Home
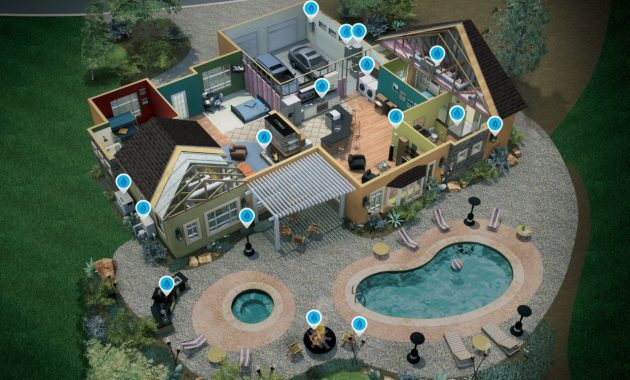
Natural Gas is one of the principal sources of energy for many of our day-to-day needs and activities.
Natural Gas Heating System
Consumers strongly prefer heat from natural gas because it is comfortable, convenient, effective and reliable.
From top-of-the-line furnaces that reach efficiency standards of more than 90 percent, to reasonably priced units that meet or slightly exceed the minimum efficiency requirement of 78 percent, today’s heating systems provide amazing options for contractors, builders and homeowners, so that consumers do not have to pay for more efficiency than they need.
Natural Gas Water Heater
In a typical home next to the heating system, water heaters are the second largest consumers in electricity. Natural gas water heaters, on average, cost less than electric water heaters and can heat water twice as quickly. In fact, for the same cost as a single bath with water heated using electricity on average, consumers can enjoy two bathtubs full of water with natural gas.
Bathroom
Smart low-flow showerheads help you conserve water and energy by letting you know when your shower is ready when the water reaches a warm temperature
Kitchen
Cook meals quicker, easier, and cheaper with instant, precise temperature control and even heat
Laundry Room
Natural gas clothes dryers are the economical option in addition to using less energy to dry clothes fast.
Fireplace
Safe, convenient and easy to use. Much cleaner and up to 99% efficient compared to wood
And there’s a lot more natural gas installed in the homes. In essence, natural gas has many advantages and makes life easier. In addition to our understanding of the natural gas distribution system, we provide a short video explaining what natural gas is.
Thus, the explanation of natural gas, its source, benefits for human life, also includes how the natural gas distribution system works. If you know the technology of natural gas, or you may be a natural gas engineer, you can provide additional information to the readers here.


