During the warm summer, have you ever been in a car and turned the AC on only to find that the air never seems to chill? Often, an air conditioning device for vehicles needs to get a boost with age. Here’s how it can be done on your own.
Air conditioning systems work at elevated pressures in cars. A failure to service the AC system properly can lead to injury. These instructions are meant to be used only as guidance, to always obey the instructions of the manufacturer where possible and to proceed at your own risk.
Car AC System
One or more of three possible candidates can be traced to most AC system problems:
- Poor level of refrigerant due to age
- Poor amount of refrigerant due to leakage
- Compressor Poor AC
If the air of your car used to blow cold and has had a declining impact quite steadily over the years, then your car probably falls into the first category and only needs refreshment from a refrigerant. However, there is a leak in the system that should be fixed if it seems that you have to recharge the AC system annually. If the AC compressor of your car is bad, no amount of refrigerant can help. You are in for some expensive repairs.
Since something past the first category is beyond the skill of most backyard mechanics, and we will stick to a basic recharge of the AC system due to the inherent hazards of novices dealing with AC systems.
If your AC problem is not solved by a quick recharge, then take it to a shop that is fully equipped to support AC systems.

What refrigerant type?
If your vehicle was designed before 1994, the AC system is likely to use R12 coolant (commonly called Freon-12). Owing to its harmful impact on the ozone layer, R12 was banned. Later vehicles use CFC-free R134a refrigerants which do not damage the environment as the older R12 did.
You would most likely not be able to legally recharge the device if your car uses R12 refrigerants. In order to handle R12 refrigerant, you must be EPA certified and, due to its lack of production, R12 is extremely costly.
However, not all is lost, as there are R134a retrofitting conversion kits. Usually, these kits are not cheap because they replace much of the AC system, but allow you to keep your air cool.
You can recharge the machine yourself if your vehicle picks up the popular R134a refrigerant. There are a few items you will need to purchase from an auto parts store:
- One or more of the refrigerant R134a cans
- AC recharge kit
- A Recharge Kit with a Pressure Gauge (Optional but highly recommended)
You need to ensure that the device has the correct pressure when recharging the AC system; too low and the AC compressor will not work, too high and the can of coolant you are using to recharge the system will burst in your hand! It’s not a bad idea to get a Smart Charger that costs about $40. To take the guess out of how much refrigerant to bring into your device.
How Your Car’s AC System Works
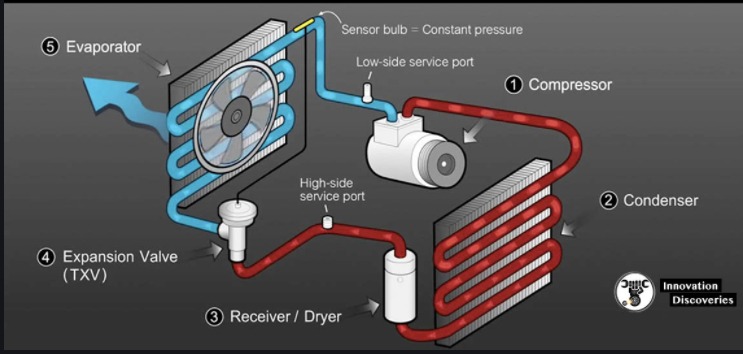
Here is a summary of how a vehicle AC system works
The heart of the AC system is the Compressor. It compresses refrigerant that is in its gas form and pumps it.
Compressor
The Compressor is powered by the drive belt of the vehicle, but if the compressor is not required, even when the engine (and belt) is working, it also has a clutch to disengage. Often when it’s running (especially when idling), you can hear an audible click coming from the front of your car. This noise is probably the clutch that triggers the AC compressor. The refrigerant with pressurized gas is pumped to
About the Condenser
The condenser is somewhat similar to the radiator for the car cooling system. In fact, the condenser is located directly in front of the radiator in most automobiles. In the condenser, the gas refrigerant expels its heat and becomes a liquid refrigerant by the time it reaches the bottom of the condenser. The liquid coolant is now pressurized as it moves.
Evaporator
Much like the condenser, the evaporator is very similar. The liquid coolant in the car is warmed by the air and boils (refrigerant has a very low boiling temperature). It sucks heat from the car’s cabin as the refrigerant converts into a gas, cooling it in the process. The evaporator often serves as a dehumidifier, so you can always notice water dripping from under the passenger side of the vehicle on wet days when the AC of the vehicle has been working. This is condensation and is completely natural.
An accumulator
On several AC systems, an accumulator is found. Its primary purpose is to store liquid refrigerant and ensure that the compressor receives only gas refrigerant. An AC compressor is meant to compress gas, not liquid, so it can be harmed if too much liquid refrigerant gets to the compressor.
Instructions Approaches
- Find your AC Valve for Low Pressure. There is a low pressure and high pressure side of any AC system. On the hose that goes from the accumulator or evaporator to the compressor, the low pressure valve would be on. On the hose that goes from the compressor to the condenser or the condenser to the evaporator, the high pressure valve would be mounted. The blue cap in the image is the low side valve.
For hooking it up to the right valve, follow the instructions that come with the smart charger. In this scenario, the valve of the smart charger won’t fit into the high pressure AC valve, so you’re playing with the wrong hose if it doesn’t fit correctly!

- As seen, insert the included AAA batteries into the ac recharge kit ( smart charger )

- Start the car and transform the AC to the max. Also, turning down the windows is not a bad idea, because the compressor won’t shut down.
- Attach the blue hose of the smart charger to the low pressure valve until the vehicle is driving and the smart charger is on. Click and hold a second or two on the black button and then release it.
Your AC system will now be diagnosed with a smart Charger. Refer to the rules that come with it on what to do if those lights come on.

- Shake a can of refrigerant and screw the can into the base of the smart charger when the car is still running and the AC is still on, if the White “Low Charge” Light Illuminates after diagnosing the device.

- Squeeze the black button for 15 seconds until the can is attached, and then release it to re-diagnose the device.
- Check the vents regularly to feel if the air is getting hotter.
- If the air isn’t any cooler after the first can of refrigerant, consider consulting a specialist. Emptying a 12 oz can of refrigerant should take about 1 minute.
SURE NOT TO TIP CAN UPSIDE DOWN, it will leak out of the refrigerant. As refrigerant can cause frost bite in seconds, you should wear gloves and eye protection.
Summary
- Find the valve on your AC system’s LOW pressure side
- Turn the car on and set the AC to Full.
- Attach to the LOW pressure valve the smart charger
- To diagnose the AC scheme, press the black button on the smart charger
- Screw a bottle of refrigerant into the smart charger if the device is tiny,
- Hold the black button for 15 seconds and then release the AC system for diagnosis; repeat until the AC system has a sufficient charge.
Conclusion
While repairing the AC system of a car is possibly well out of the DIY’s reach, he or she can recharge a refrigerant-low system. To avoid overloading the device, it would be prudent to buy some form of charging kit that has either a digital or analog gauge. If you still have issues or notice that you often need to recharge the system, then take the car to a shop equipped to work on AC systems. To help locate any leaks and repair any other issues, they will add dye to the refrigerant.